What materials are used in 3D printed insoles?
3D printing technology has dramatically changed the way insoles are produced. Whereas traditional insoles often consist of composite layers of foam, cork or plastic, 3D printing offers new possibilities with innovative materials. The choice of material determines not only the durability and support of the sole, but also its comfort and adaptability to individual needs.
What materials are used in 3D printed orthotics? And what properties make these materials suitable for podiatric applications?
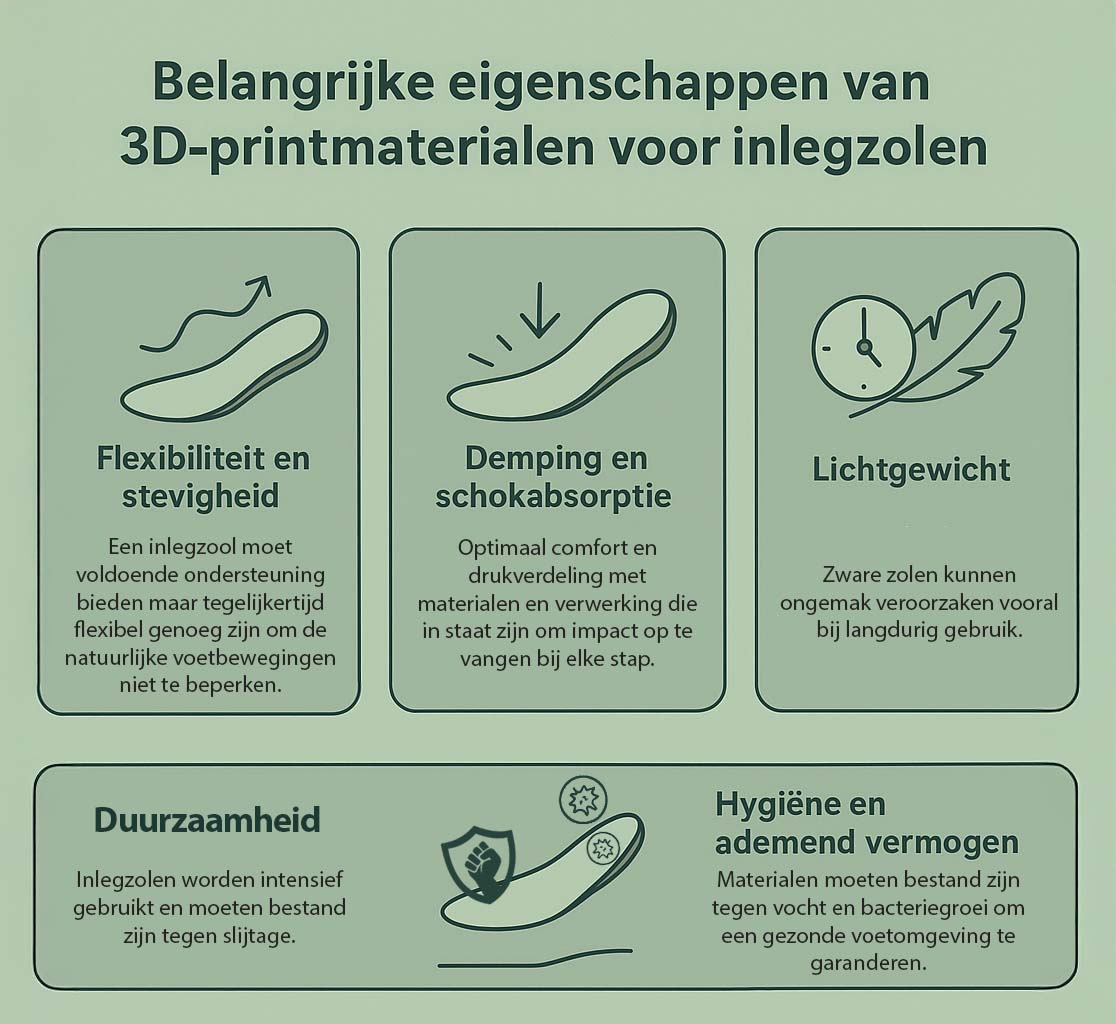
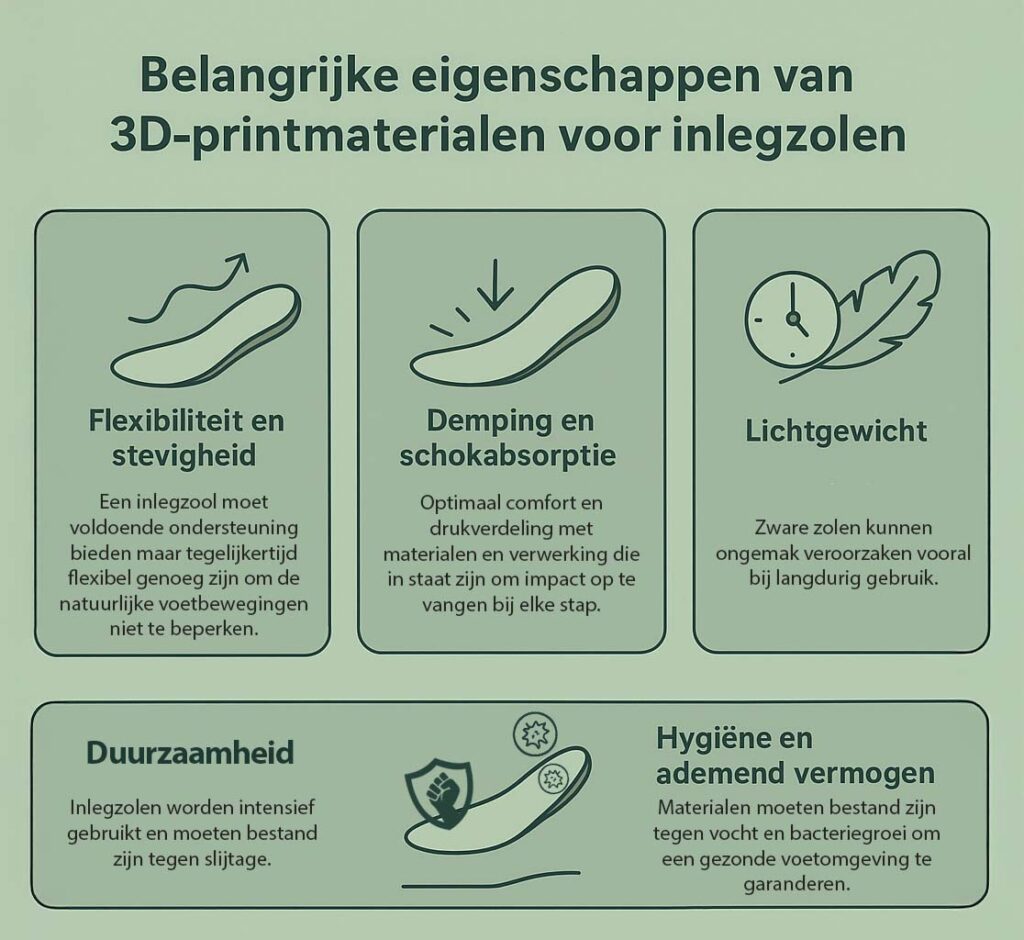
Important properties of 3D printing materials for insoles
A sole must meet specific requirements to be effective. Therefore, 3D printing materials are selected based on the following characteristics:
- Flexibiliteit and firmness – An insole should provide sufficient support, but at the same time be flexible enough not to restrict natural foot movement.
- Damping and shock absorption – For optimal comfort and pressure distribution, materials must be able to absorb impact. Did you know that with 3D printed soles you can create different hardnesses create in 1 printed sole?
- Durability – Insoles are used intensively and must withstand wear and tear.
- Lightweight – Heavy soles can cause discomfort, especially with prolonged use.
- Hygiene and breathability. – Materials must be resistant to moisture and bacterial growth to ensure a healthy foot environment.
Commonly used materials for 3D printed insoles
1. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane).
TPU is one of the most widely used materials for 3D printed insoles. It combines flexibility with strength, making it ideal for everyday, sports and medical applications.
Advantages of TPU:
- Good balance between flexibility and support
- Hard-wearing and durable
- Resistant to moisture and bacteria
- Lightweight and comfortable
TPU is often used in soles that require different zones with different hardnesses. This can be accomplished within one printing process, giving the sole optimal pressure distribution.
2. PA (Polyamide) – Nylon
Polyamide, better known as nylon, is a commonly used material in SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) 3D printing technology. It is a sturdy and wear-resistant material suitable for long-term use.
Advantages of PA/Nylon:
- Very strong and durable
- Resistant to high loads
- Lightweight
- Good chemical and thermal resistance
Nylon is often chosen for soles that require extra strength and structural integrity, for example, in heavy-duty or medical applications.
3. TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer).
TPE is similar in properties to TPU, but it is even more elastic and offers a softer wearing feel. This material is often used for orthotics where extra cushioning and flexibility are desired.
Advantages of TPE:
- High elasticity
- Excellent shock absorption
- Comfortable and flexible
- Resistant to tearing and abrasion
TPE is ideal for soles intended for athletes or people with sensitive feet who need extra comfort.
4. SLA resins (Resin for Stereolithography).
SLA resins are less commonly used for insoles, but offer advantages for precision printed parts. These resins are cured with UV light and can be tailored to specific needs.
Benefits of SLA resins:
- Very high level of precision and detail
- Smooth finish without finishing
- Suitable for medical applications
What material do we recommend for podiatrists?
For podiatrists transitioning to 3D printed insoles is TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) the best choice. This material offers an optimal balance of flexibility and firmness, making it suitable for everyday applications as well as sports and medical orthotics.
In addition, 3D printing with TPU makes it possible to produce soles directly in the field without post-processing. This saves time and ensures consistent quality without depending on external suppliers.
For podiatrists looking for an efficient, durable and high-quality solution, TPU is the ideal choice.
Wondering what PodoPrinter can do for your practice?
Would you also like to benefit from the advantages of 3D printed soles? Then contact us for a no-obligation demonstration of our SOLE by printer. Call [ +31 (0)40 3410900] or fill out the contact form.
How podiatrists save 20% time with 3D printed insoles
Podiatrists work daily to improve their patients' posture and mobility. Insoles play an important role in this effort, but making and ordering them is time-consuming. Methods, such as manual adjustments or CNC milling, involve dust, noise and waste. Fortunately, there is an innovative solution: 3D printed soles. This will save you time, improve efficiency and keep more control over your production process.
The problem: time-consuming production and dependency
Many podiatrists run into the same problems when producing or sourcing insoles:
- Time-intensive manual labor
Sanding, gluing and finishing soles is time-consuming and requires precision. This comes at the expense of time that can be spent on patient care. - Dependence on external suppliers
When soles are outsourced to an outside partner, it means waiting time. Delivery can take days, and if there is an error in sizing or finishing, the entire order must be redone. - Lots of waste and unhealthy working conditions
CNC milling works with large blocks of material of which up to 95 percent becomes waste. In addition, the process creates a lot of dust and chemical fumes from adhesives and coatings. This is not only bad for the environment, but also for the health of the handler.
How 3D printed insoles save time
With a 3D printer for soles, such as the MODULA from PodoPrinter , you bring all production in-house. This provides significant benefits:
- Automation of the production process
The 3D printer makes soles without manual sanding or gluing. This saves time and reduces physical strain. - Faster delivery time and less dependency
Because you control production yourself, you no longer have to wait for outside suppliers. This means that soles are ready for use immediately, without additional transportation costs or long delivery times. - Consistent quality without manual errors
Manual adjustments lead to slight variations in the finish of soles. With a 3D printer, each pair is printed identically and exactly to specification, improving quality and fit. - Cleaner and healthier work environment
A 3D printer operates without milling dust and harmful glue fumes. This makes for a safer workplace and less need for expensive exhaust systems. - Less waste and lower costs
Instead of milling out a large block of material, the printer uses exactly the amount of raw material needed. This not only saves costs, but is also more sustainable.

What does this mean for daily practice?
By switching to 3D printed soles, podiatrists can work more efficiently and help more patients without employing additional staff. The time savings add up to 20 percent, which amounts to a full working day per week. This gives room to schedule more consultations or just reduce the workload.
In addition, 3D printing offers new possibilities. For example, it is possible to integrate different hardnesses within one sole, allowing for even better support. Patient data can also be printed directly into the sole, so there is never any confusion about which soles belong to which patient.
More control and less loss of time
Innovations in healthcare increasingly revolve around efficiency and customization. 3D printed soles fit perfectly within this trend. They make production faster, cleaner and less dependent on external parties.
For podiatrists looking to optimize their workflow, reduce costs and create a healthier work environment, 3D printing is a logical next step. The move means not only more efficient practice operations, but also an improved patient experience.
Want more control over your production and less time wasted on manual adjustments? Then 3D printing is the future for your practice.
Wondering what PodoPrinter can do for your practice?
Would you also like to benefit from the advantages of 3D printed soles? Then contact us for a no-obligation demonstration of our Modula.
What is the difference between standard and 3D printed insoles?
Insoles are an essential tool for people with foot pain, posture problems or strains. Traditionally, insoles have been custom-made via manual operations or CNC milling machines. Today, 3D printing technology offers a solution that benefits podiatrists and patients alike.
What are the main differences between standard soles and 3D printed soles? And why are more and more podiatrists choosing this modern production method?
How are standard insoles made?
Traditional soles are produced in a variety of ways. The most common methods are:
- Manual manufacture: A podiatrist manually adjusts an existing sole by sanding, gluing and possibly hardening it with a top coat. This process is labor intensive and can take a lot of time per pair.
- CNC milling: In this method, a sole is milled from a block of material based on a digital scan. Although this process is automated, it results in a lot of waste. In fact, up to 95 percent of the material used is discarded.
- Prefabricated soles: Some suppliers offer standard soles with slight modifications, but these offer less customization and optimal support than fully custom-made soles.
While these methods have proven their worth, they also present challenges. The manual process is time-consuming, CNC milling is not sustainable and external production causes delays and additional costs.
How do 3D printed insoles work?
3D printing involves building a sole layer by layer from a special material, based on a digital scan. This process offers several advantages over traditional methods:
- Full customization without manual finishing: Because the sole is printed directly to specification, sanding, gluing and adjustment are unnecessary. This saves time and increases precision.
- Less waste: Unlike CNC milling, where large parts of the material are lost, 3D printing uses only the material needed. This makes the process more sustainable.
- Possibility of combining different hardnesses: A 3D printer allows different areas within a single sole to vary in hardness. This means that certain parts of the sole are firmer, while others offer more cushioning. With traditional soles, this is often not possible without adding extra layers.
- Faster production and less dependence on suppliers: Because 3D printers can be used in-house, podiatrists no longer have to wait for external deliveries. This increases flexibility and reduces lead time from diagnosis to delivery of the sole.
- Cleaner and healthier work environment: 3D printing does not release sanding dust or glue fumes, providing a safer working environment without the need for additional exhaust systems.
 Why switch to 3D printed soles?
Why switch to 3D printed soles?
Podiatrists who switch to 3D printing technology not only save time, but also improve the efficiency of their practice. In fact, many podiatrists run into the following problems:
- Time loss due to manual post-processing
- Delays due to outsourcing to CNC milling
- High cost of waste disposal and external production
- Unhealthy working conditions due to dust and glue odors
A 3D printer, such as the Modula, solves these problems. The printer allows podiatrists to produce custom orthotics directly in the practice, with minimal rework and without relying on outside parties. This results in time savings averaging 20 percent, which equates to a full workday per week.
Wondering what PodoPrinter can do for your practice?
Would you also like to benefit from the advantages of 3D printed soles? Then contact us for a no-obligation demonstration of our Modula.